 Categories
Categories 
Gemstones and jewelry are an integral part of investment today. The gemstone market is estimated to grow to over $50 billion by 2032. However, factors like luxury and personalization are key drivers for the growth of the market, and still finds itself struggling with issues of authenticity. One problem that is significant in this segment is counterfeit.
Read More: Gemstone Industry & Market Trends
For instance, a green gemstone sold as emerald stone could actually be a lower-value stone like peridot or glass, misleading buyers and reducing trust in the market.
People are random victims of purchasing fake gemstones, leading to a loss of their money. In this context, legitimate sellers following rules and regulations are also unwittingly affected.
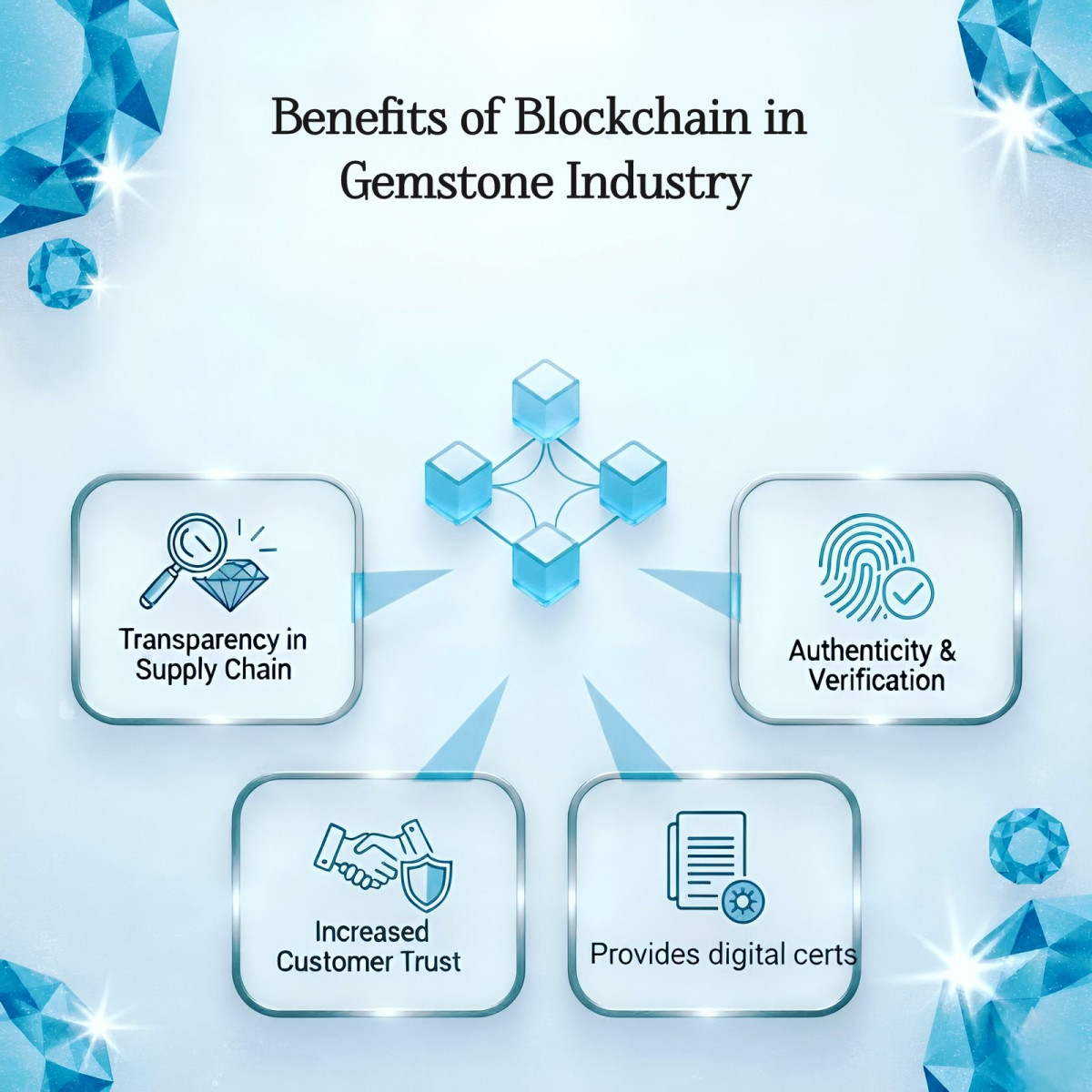
To solve this problem, blockchain has come up as a revolutionary game-changer.
Buying a gemstone should feel exciting, but for many people, it becomes stressful. The biggest reason?
This is where blockchain comes in. It is a long-known procedure where trust is the key. To connect it with gemstones, the process starts with a digital notebook. From the time the gem is mined to the end process where it is being set in a jewellery piece, everything is documented. This record is clear and cannot be altered. So the sellers know the gem’s journey, and they can build trust with their customers.
Learn More: Don’t Get Fooled: 7 Things Every First-Time Gemstone Buyer Must Know
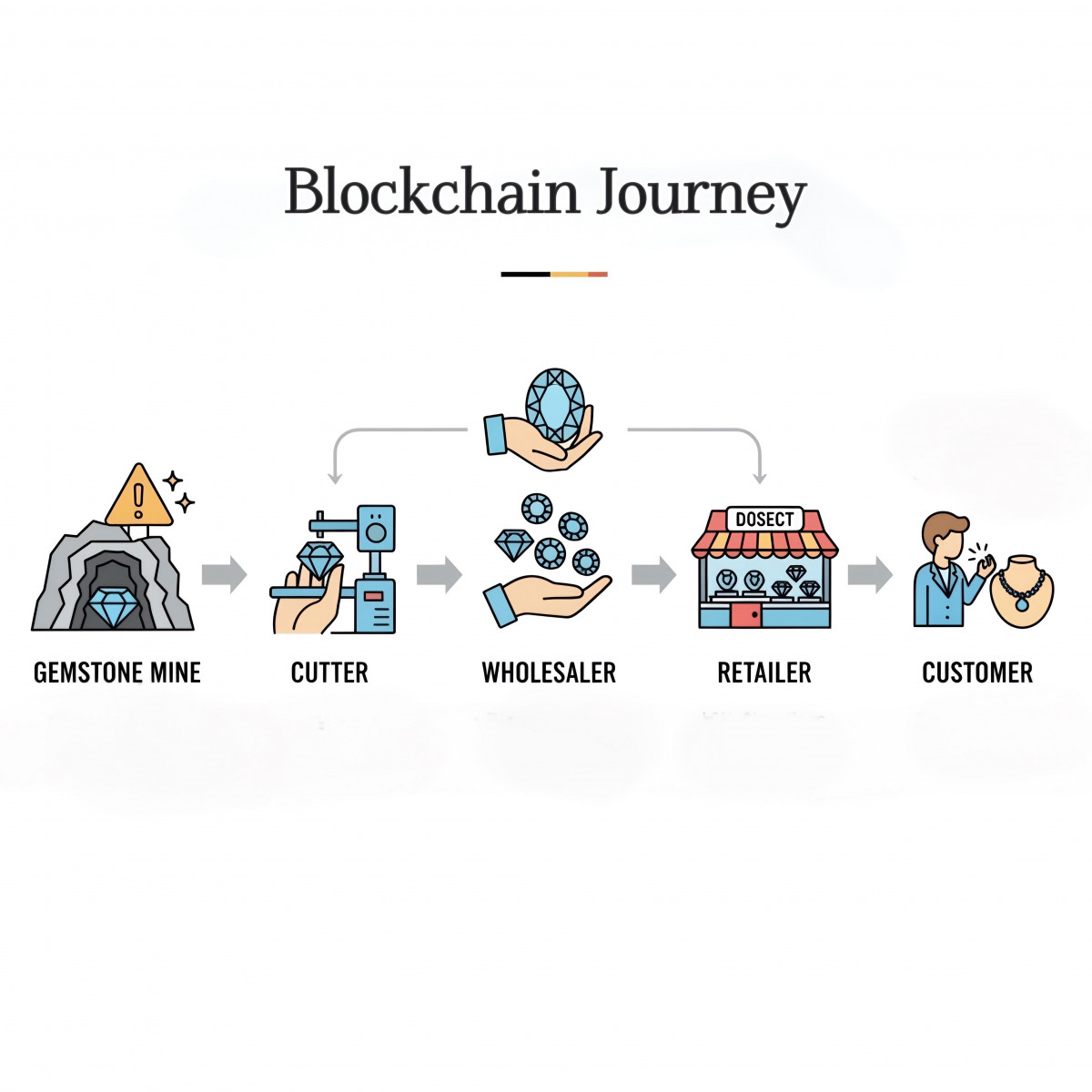
Here is a small breakdown of this process:
Mining – Knowing details like gemstone origin and weight is important. Thus, it is noted down first.
Cutting & Treatments – If the gem is cut, polished, or treated, that information gets added to the digital book.
Certification – Reports from gem labs can be linked directly, so buyers don’t have to worry about fake certificates.
Ownership – Each time the stone is sold, the change in ownership is recorded.
Final Purchase – When the customer buys it, they can simply scan a code or use an app to see the gem’s full journey.
Some gemstones are often linked with blockchain projects because they are valuable, in high demand, and often copied or faked. These include:
Blue Sapphires: These are the most desirable gemstones. In Indian culture, these are highly valued stones. Certain blue gemstones that are affordable are faked as blue sapphires. Blockchain technology helps identify their origin and authenticity.
Emeralds: These green gems are famous but often treated to improve their look. Blockchain makes it clear whether an emerald is natural or treated.
Read Further: Comparison of Natural and Synthetic Emerald Properties
Rubies: The rare pigeon blood rubies are among the costliest stones. Blockchain helps buyers know they are getting a real ruby stone and not a synthetic one.
Diamonds: Not a colored gem, but diamonds were the first to use blockchain on a large scale through projects like De Beers’ Tracr.
This set the example for others. Aquamarine stone and Amethyst : Even though these are not as pricey as rubies or sapphires, they are also starting to be tracked with blockchain to give buyers more trust.
Blockchain ensures trust for buyers and credibility for sellers. Earlier, diamonds were the only leading the way, but now colored gemstones like sapphires, rubies, and emeralds are also linked with blockchain technology.

How to Clean Gemstone Jewelry Naturally: Easy & Effective Tips
December 5th, 2025

Gemstone Jewelry Forecast: What Stones & Styles Will Dominate in 2026?
December 1st, 2025
Why Shani Can Make or Break Your Life — The Untold Astrological Truth
December 1st, 2025